Data management is crucial for modern organizations as it ensures that data is accurate, accessible, and secure, enabling informed decision-making and operational efficiency. In an era where data is often referred to as the “new oil,” effective data management practices are essential for maintaining a competitive edge.
For example, Airbnb has launched “Data University,” which equips employees with skills in data analysis and visualization. This initiative has resulted in a significant increase in the use of the company’s central database, with 45% of employees becoming active users weekly. Such empowerment fosters a culture of data-driven decision-making, enhancing operational competence and strategic planning.
Similarly, another example being Wells Fargo established the Enterprise Data League to create a centralized repository for accurate organization-wide data. This initiative minimized inconsistencies in data entries and improved reporting accuracy, ultimately facilitating better decision-making and operational efficiency across departments.
These examples gives a clear idea of managing the data in organizations will not only enhance the operational efficiency but also the customer trust. Today, as all the organizations are largely depending on the data it equally becomes crucial to manage it as well.
Understanding Data Management and its importance
Data management can be defined as the practice of collecting, organizing, managing, and accessing data to support productivity, efficiency, and decision-making within an organization. It involves a comprehensive set of disciplines aimed at maximizing the value of data throughout its lifecycle.
Data Management Processes
The core processes involved in data management include:
1. Collection: Gathering data from various sources, including internal systems and external inputs.
2. Storage: Safely storing data in databases or data lakes to ensure it is accessible when needed.
3. Access: Providing users with the ability to retrieve and utilize data efficiently.
4. Security: Implementing measures to protect data from unauthorized access and breaches, ensuring compliance with regulations.
Importance of Robust Data Management Strategy
A robust data management strategy is crucial for enhancing decision-making by providing accurate and timely information. It improves operational efficiency by streamlining processes, reduces redundancy, and boosts productivity. Moreover, it ensures compliance with legal and regulatory requirements regarding data handling and privacy, while facilitating data integration for a comprehensive view of organizational performance.
The Role of AI in Data Management
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is transforming data management by automating various tasks and enhancing the efficiency, accuracy, and speed of data processing and analysis. This integration is crucial as organizations face an exponential increase in data generation and complexity.
AI Technologies in Data Management
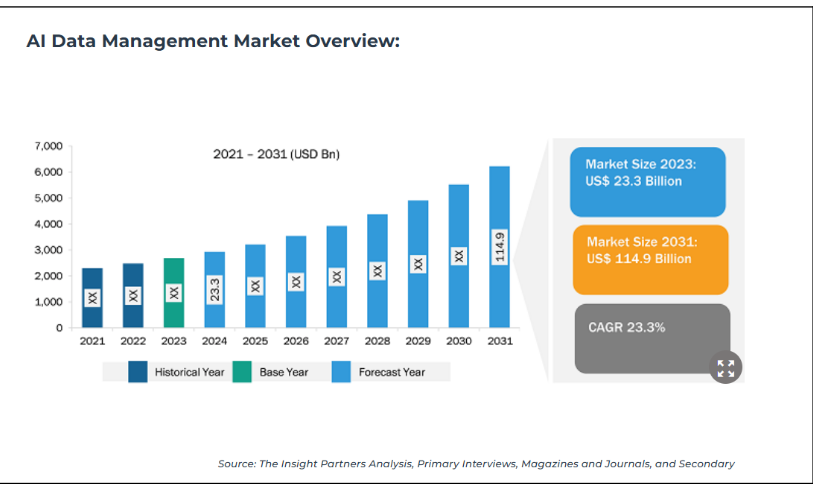
The global AI data management market was valued at approximately $25.53 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 22.7%, reaching around $114.99 billion by 2031. This growth is fueled by the increasing reliance on data-driven insights across various sectors, including finance, retail, and government.
Overview of AI Tools:
1. Machine Learning (ML):
ML algorithms automate tasks such as data cleansing, classification, and anomaly detection. These algorithms can learn from historical data to improve their accuracy over time, making them invaluable for maintaining data quality and integrity.
2. Autonomous Databases:
These databases leverage AI to perform self-management tasks, including tuning, patching, and scaling without human intervention. This reduces the operational burden on IT teams and enhances system reliability.
3. Natural Language Processing (NLP):
NLP techniques enable better text data management by facilitating tasks like sentiment analysis, text classification, and information extraction from unstructured data sources.
4. Predictive Analytics:
AI models analyze historical data to forecast future trends, aiding businesses in decision-making processes by providing actionable insights based on data patterns.
5. Generative AI:
This type of AI can create synthetic datasets that mimic real-world data distributions, which can be useful for testing algorithms or filling gaps in existing datasets.
Implementing AI-Powered Tools
Choosing the Right Tools
When selecting AI-driven data management solutions, several criteria should be considered:
1. Automation Capabilities: Look for tools that offer robust automation features. For example, Zapier allows users to create automated workflows (called Zaps) across thousands of applications, enabling seamless integration and task automation without coding expertise
2. Ease of Use: User-friendly interfaces are crucial for adoption. Tools like Asana provide intuitive project management features enhanced by AI, helping teams set smart goals and identify workflow blockers with minimal training.
3. Integration Potential: Ensure the tool can integrate with existing systems. Oracle’s AI-powered Supply Chain Management offers real-time visibility and integrates with various platforms to optimize supply chain operations.
4. Scalability: Choose solutions that can grow with your business. For instance, IBM Watson Supply Chain provides customizable dashboards and predictive insights that can adapt as your operations expand.
Challenges/Common Pitfalls in Data Management
Effective data management is crucial for organizations aiming to leverage data for strategic decision-making. However, several challenges can impede this process, including data silos, compliance issues, and resistance to change. Listed Below is an exploration of these challenges, their implications.
1. Data Silos
Data silos occur when departments or teams within an organization store data in isolated systems that are not easily accessible to others. This fragmentation can arise from various factors, including outdated legacy systems, departmental autonomy, and a lack of collaboration between teams. Often this leads to
2. Inconsistencies: Data silos cause conflicting data versions across departments, leading to flawed decision-making.
3. Reduced Collaboration: Limited data sharing hampers cross-departmental collaboration and insights.
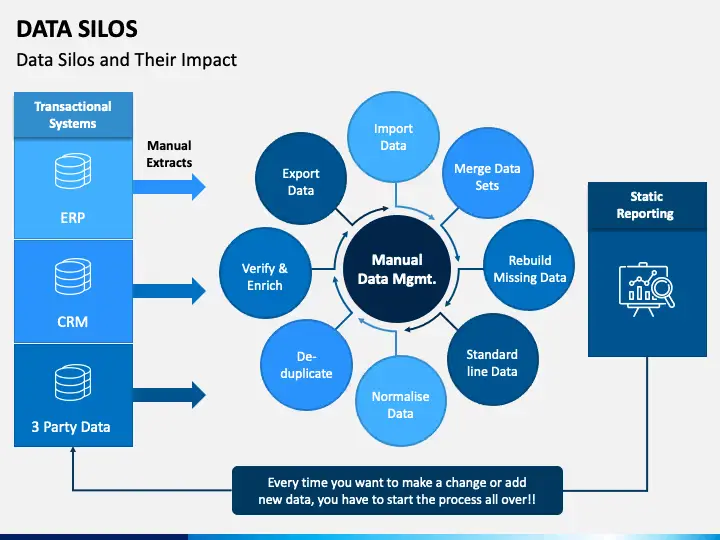
Source: Estuary
Compliance Issues
Organizations face significant compliance challenges when managing data across silos. The lack of a unified data management strategy complicates compliance with regulations such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and other data privacy laws. This leads to,
1. Manual Reporting Errors: Compliance reporting requires manual data aggregation from various silos, increasing the risk of errors and omissions.
2. Data Security Vulnerabilities: Inconsistent security protocols across systems expose sensitive information to breaches, complicating compliance with data protection regulations
Resistance to Change
Implementing effective data management practices often requires cultural shifts within organizations. Employees may resist changes that involve new technologies or processes due to comfort with existing practices.
Challenges-
1. Fear of Job Displacement: Employees might fear that new data management initiatives could threaten their roles or require them to learn new skills.
2. Lack of Engagement: Without strong leadership support and clear communication regarding the benefits of change, employees may remain disengaged from initiatives aimed at improving data sharing and collaboration.
Leveraging Data Insights: Prescience’s, a Movate company Role in Strategic Transformation for Manufacturing Enterprises
A leading textile machinery manufacturer struggled with data availability and synchronization across legacy systems, leading to delays in BI reports and forecasting spare parts demand. Partnering with Prescience Decision Solutions, a Movate company, they implemented a comprehensive Data Management and BI platform, developing a data strategy, assessing cloud options, and identifying 37 improvement activities in three Agile phases. This solution accelerated real-time decision-making, enabled self-service reporting, and uncovered over 60 new KPIs and 9 analytics opportunities, enhancing operational efficiency and collaboration.
To know more in detail click here.
Final take
In conclusion, an effective data management is not merely a technical necessity but a strategic imperative that drives innovation and growth. By prioritizing robust data management practices, organizations can unlock valuable insights, enhance operational efficiency, and build trust with customers and stakeholders alike. As businesses continue to evolve in an increasingly complex digital environment, the ability to harness and manage data effectively will remain a cornerstone of success.

Prescience Team



